AI Invoice Processing: The Complete Technical Guide 2026
AI invoice processing cuts costs by 80% and achieves 95-99% accuracy. Complete technical guide to implementation, ROI, and choosing the right solution.

Processing invoices manually costs businesses an average of $22.75 per document. When you're handling hundreds or thousands of invoices monthly, that number quickly becomes unsustainable. AI invoice processing has emerged as the solution that companies across industries are adopting to cut costs, eliminate errors, and accelerate their accounts payable workflows.
This technology isn't just about faster processing. It's about fundamentally changing how businesses handle financial documents. Modern AI systems can extract data from invoices with 95-99% accuracy, reduce processing time from 10 minutes to under 30 seconds per invoice, and seamlessly integrate with existing accounting systems without requiring templates or complex configurations.
If you're already using email invoice automation, AI processing takes that efficiency to the next level by eliminating the manual review step entirely.
What Makes AI Different from Traditional Invoice Processing
Traditional invoice processing relies on manual data entry or basic Optical Character Recognition (OCR) systems. Someone receives an invoice via email, opens it, and manually types vendor names, amounts, dates, and line items into an accounting system. Even with standard OCR, the technology can only recognize characters without understanding context or structure.
AI invoice processing fundamentally changes this approach. Instead of simply reading text, AI systems understand what they're looking at. They can interpret an invoice's structure, distinguish between different data types, and extract information accurately even when layouts vary dramatically between vendors.
The technology works through a combination of computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning models that have been trained on millions of invoice examples. When an invoice arrives, the AI doesn't need predefined templates or rules. It analyzes the document, identifies relevant fields, extracts the data, and validates it against business logic, all in seconds.
This contextual understanding makes all the difference. Traditional OCR might read "1,234.56" as text, but AI knows whether that number represents a total amount, a line item price, or a purchase order number based on its position and surrounding context. For businesses processing invoices from Gmail, tools like automated invoice extraction from Gmail leverage this AI capability to handle documents directly from your inbox.
The Core Technologies Powering AI Invoice Processing
Three primary technologies work together to enable modern AI invoice processing systems. Understanding how these components interact helps explain why AI-powered solutions consistently outperform traditional methods.
Computer Vision and Advanced OCR
Modern invoice processing uses computer vision that goes far beyond traditional OCR. Instead of just converting images to text, these systems analyze document structure, identify tables, understand layout hierarchies, and maintain relationships between different data points.
Advanced OCR engines powered by AI can handle poor scan quality, skewed images, watermarks, handwritten notes, and inconsistent formatting. They maintain accuracy even when processing invoices captured via smartphone cameras at odd angles or with varying lighting conditions.
Recent benchmarks show that AI-enhanced OCR systems achieve character error rates below 2% on printed invoices and word error rates under 5% on standard business documents. This level of accuracy makes automated processing viable for mission-critical financial workflows. For a deeper exploration of how OCR converts scanned invoices into structured data step by step, see our complete guide to invoice OCR.
Machine Learning for Data Extraction
Machine learning models form the intelligence layer that makes sense of the text extracted by OCR. These models have been trained on millions of invoices to recognize patterns, understand field relationships, and adapt to new formats automatically.
Unlike rule-based systems that break when encountering new invoice layouts, ML models generalize from examples. They learn that invoice totals typically appear in certain contexts, vendor information follows specific patterns, and line items share structural similarities regardless of formatting differences.
The models continuously improve through a process called active learning. When human reviewers correct extraction errors, those corrections feed back into the training data, making the system progressively more accurate for specific document types and vendors.
Natural Language Processing for Context
Natural language processing enables AI systems to understand text meaning beyond simple pattern matching. NLP models can interpret vendor names written in different formats, recognize dates presented in various international standards, and distinguish between similar-looking data that has different business meanings.
This capability proves especially valuable when processing invoices with non-standard terminology, industry-specific jargon, or multiple languages. The AI doesn't just extract text, it comprehends what that text represents within the business context.
NLP also powers the semantic validation that catches errors traditional systems miss. For example, if an invoice lists "Net 30" payment terms but shows a due date that's 60 days out, the AI flags this discrepancy automatically.
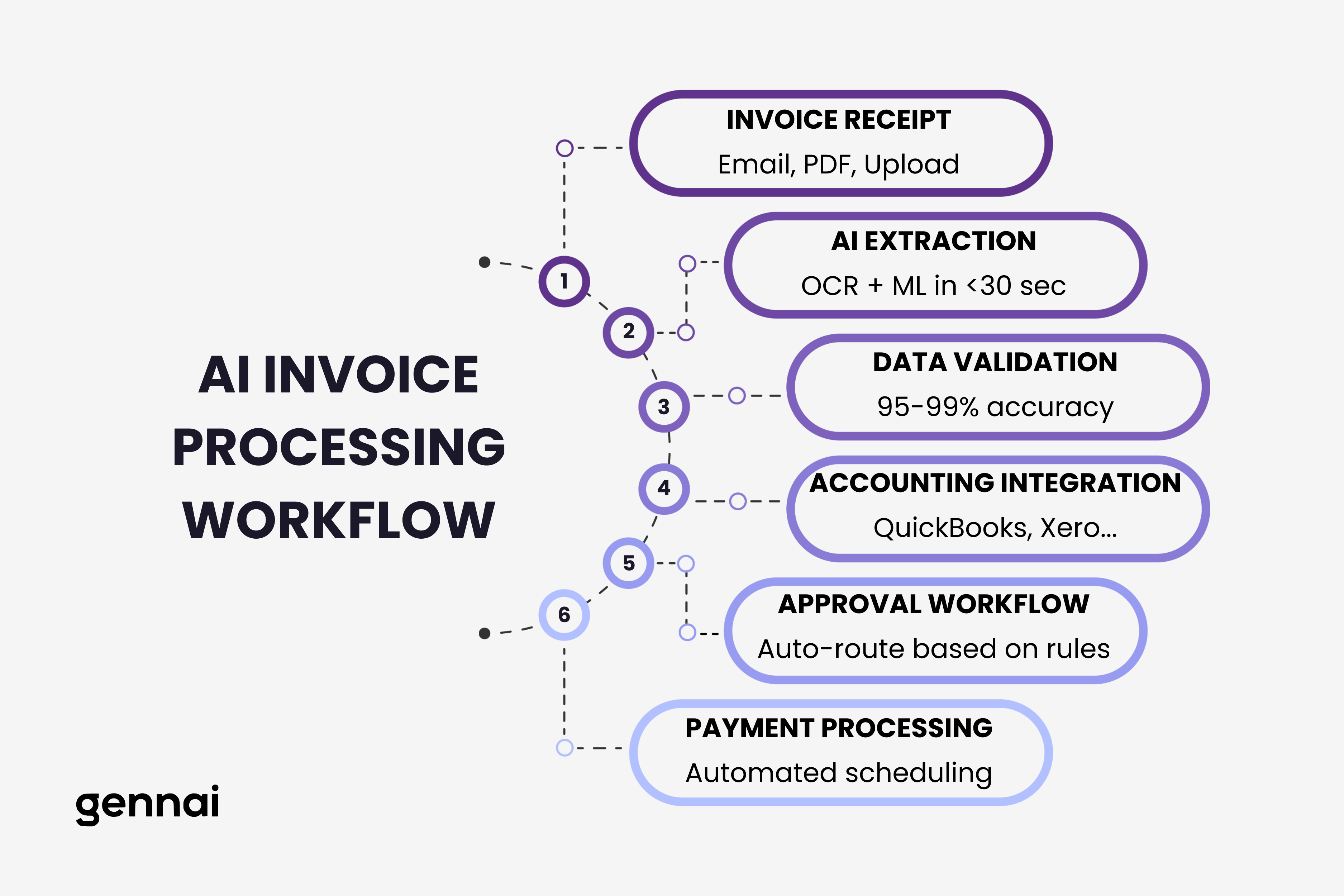
How Modern AI Invoice Processing Actually Works
The end-to-end process of AI invoice processing happens in distinct phases, each leveraging different AI capabilities to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Document Ingestion and Classification
Invoices arrive through multiple channels: email attachments, API connections, cloud storage folders, or direct uploads. The AI system's first task is identifying document types. Is this an invoice, a purchase order, a receipt, or something else entirely?
Modern systems use document classification models that analyze visual layout, text patterns, and metadata to categorize documents with over 95% accuracy. This happens in milliseconds and doesn't require users to manually sort documents before processing.
The system also assesses document quality at this stage. Poor scans or low-resolution images trigger enhancement algorithms that improve readability before extraction begins. Some advanced systems can detect when an image is too degraded for reliable processing and automatically request a better copy.
Intelligent Field Extraction
Once the system knows it's processing an invoice, specialized extraction models go to work. These models don't extract text randomly. They understand invoice structure and know what information matters for accounting purposes.
Key fields get extracted first: vendor information, invoice number, date, due date, currency, and total amount. Then the system moves to line-item details, capturing descriptions, quantities, unit prices, and line totals.
The extraction doesn't rely on fixed coordinates or templates. Instead, the AI uses contextual clues, surrounding text, and learned patterns to locate each field. This approach works across vendors without requiring setup or configuration for each new invoice format.
Field extraction includes confidence scoring. The AI assigns probability scores to each extracted value, indicating how certain it is about the accuracy. Values with high confidence can route through automated workflows, while lower-confidence extractions flag for human review.
Validation and Business Logic
After extraction, the validation phase applies multiple checks to ensure data accuracy and completeness. The system verifies that required fields are present, formats are correct, and values make logical sense.
Mathematical validation confirms that line items sum to subtotals and that tax calculations match stated rates. Duplicate detection compares newly processed invoices against historical records to prevent double payment. Policy compliance checks ensure invoices meet approval thresholds and purchasing rules.
The AI can also perform three-way matching, automatically comparing invoice details against purchase orders and receiving records. Discrepancies get flagged with specific explanations, making exception handling faster and more straightforward.
Data Export and Integration
Clean, validated data flows into destination systems through API connections or structured file exports. Modern AI platforms integrate directly with popular accounting software, ERP systems, and AP automation tools.
The integration isn't just about moving data. The AI maps invoice fields to the correct general ledger codes, cost centers, and project codes based on learned patterns from historical transactions. This automated coding can reduce manual accounting work by 70% while maintaining accuracy.
Export formats adapt to system requirements. Whether your accounting software needs CSV files, JSON payloads, or direct database entries, the AI platform handles formatting automatically.
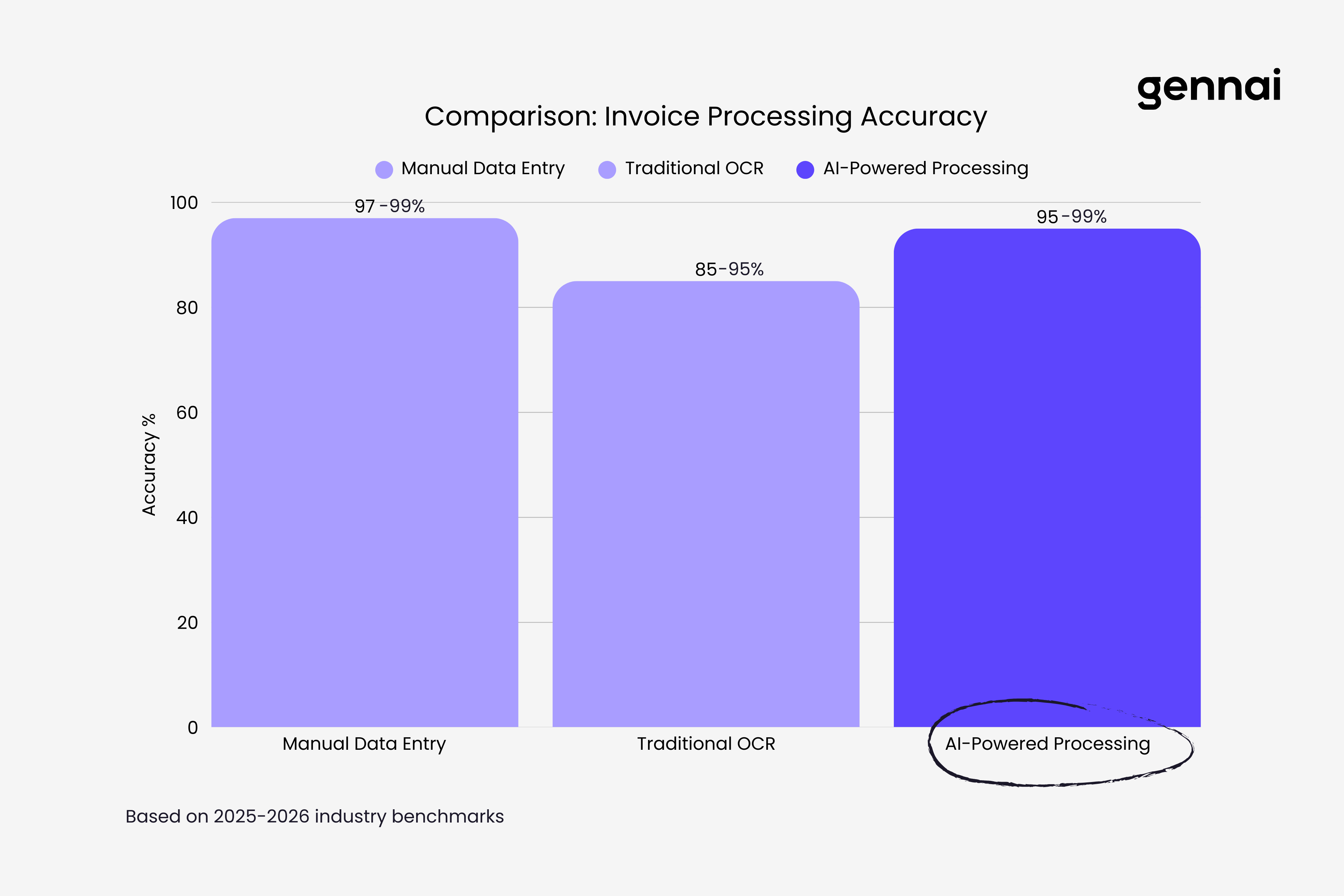
Accuracy Benchmarks and Real Performance Data
Understanding AI invoice processing performance requires looking at verified benchmarks rather than marketing claims. Independent testing provides the clearest picture of what these systems can actually achieve.
Recent benchmarks comparing leading AI models found that Claude Sonnet 3.5 achieved the highest overall accuracy across diverse invoice formats and quality levels. In tests involving invoices with varying scan quality and layouts, Claude demonstrated superior resilience, maintaining high extraction accuracy even with lower-quality source documents.
Specifically, when comparing AI models for invoice extraction, Gemini achieved 94% accuracy thanks to its integrated vision capabilities, GPT reached 91% when coupled with advanced OCR, and Claude scored 90% while showing better format consistency. These benchmarks tested extraction of key fields like vendor names, invoice numbers, dates, amounts, and line items across hundreds of real-world invoice samples.
Processing speed represents another critical metric. Manual invoice processing averages 5-10 minutes per document. AI systems reduce this to under 30 seconds, representing time savings exceeding 95%. For businesses processing 1,000 invoices monthly, this translates to approximately 130 hours saved per month.
Cost reduction proves equally dramatic. While manual processing costs average $22.75 per invoice, AI-powered systems bring costs down to approximately $2.36 per invoice. This represents more than 80% cost reduction while simultaneously improving accuracy and processing speed. Understanding the real cost of manual invoice processing helps put these savings into perspective.
Error rates tell an important story. Manual data entry produces errors in 1-3% of transactions. Each error costs an estimated $53 to identify and correct according to research from the Institute of Finance and Management. AI systems reduce error rates to 0.01-0.05%, virtually eliminating costly correction cycles.
Common AI Invoice Processing Challenges and Solutions
Even sophisticated AI systems encounter challenges. Understanding these issues and their solutions helps set realistic expectations and implement AI invoice processing successfully.
Handling Poor Document Quality
Low-resolution scans, faded text, watermarks, stamps, and skewed images all present obstacles for accurate extraction. While AI systems handle quality issues better than traditional OCR, extremely degraded documents can still cause problems.
Leading solutions employ preprocessing algorithms that enhance image quality before extraction. These algorithms adjust contrast, remove noise, correct skewing, and sharpen text. Some systems can even remove watermarks or stamps that obscure critical information.
For organizations dealing with consistently poor-quality invoices from specific vendors, the solution often involves addressing the root cause. Working with suppliers to receive invoices digitally rather than as scanned paper documents eliminates quality issues entirely.
Template Variability Across Vendors
No two vendors format their invoices identically. Fields appear in different positions, use varying terminology, and follow different structural patterns. Traditional OCR systems require manual template configuration for each vendor format, creating significant setup overhead.
AI invoice processing solves this through template-free extraction. Machine learning models trained on diverse invoice examples can generalize to new formats automatically. The system doesn't need to know where the invoice number appears because it understands what an invoice number looks like in context.
This flexibility becomes crucial as businesses scale. Companies working with hundreds or thousands of vendors can't afford to maintain templates for each one. AI systems that adapt automatically to new formats make invoice processing viable at scale.
Multi-Page and Complex Invoices
Simple invoices fit on a single page, but complex service agreements, detailed project billing, and large purchase orders often span multiple pages. These documents require the AI to maintain context across pages, understand table continuations, and properly aggregate totals.
Modern AI systems use document understanding models that treat multi-page invoices as cohesive units rather than independent pages. They track table structures across page breaks, associate line items with correct headers, and identify which totals represent page subtotals versus document totals.
Line-item extraction for complex invoices with dozens or hundreds of items presents its own challenge. Advanced systems can extract entire tables while preserving relationships between columns, identifying which values represent descriptions, quantities, prices, and totals.
Handwritten and Mixed-Format Documents
Some invoices contain handwritten notes, corrections, or additional charges added after printing. AI systems need to process both typed and handwritten text accurately.
Computer vision models trained specifically on handwriting recognition handle this challenge. These models can distinguish handwritten text from printed content and extract both with appropriate confidence scores. Values extracted from handwritten sources typically flag for human verification given the higher error potential.
Mixed-format documents that combine tables, free text, checkboxes, and signatures require specialized processing. Document understanding AI can segment these different content types and apply appropriate extraction techniques to each section.
Integration with Existing Business Systems
AI invoice processing delivers maximum value when it integrates seamlessly into existing workflows. The technology shouldn't exist in isolation but should connect with the accounting software, ERP systems, and payment platforms companies already use.
Accounting Software Integration
Direct integration with platforms like QuickBooks, Xero, NetSuite, and SAP ensures invoice data flows automatically from extraction to posting. Modern AI platforms offer pre-built connectors for major accounting systems, eliminating custom development work.
The integration handles not just data transfer but also field mapping, GL code assignment, and vendor matching. When processing an invoice from a known supplier, the system automatically links to the existing vendor record, applies default GL codes, and routes for appropriate approval based on business rules.
Two-way sync capabilities mean changes made in either system stay synchronized. If an accountant adjusts an invoice amount in the accounting system, that change reflects in the invoice management platform. This bidirectional communication prevents discrepancies and maintains a single source of truth.
Businesses evaluating different platforms should review comprehensive guides like our invoice management software buyer's guide to understand integration requirements and capabilities across different solutions.
ERP System Connectivity
Enterprise resource planning systems like Microsoft Dynamics, Oracle ERP Cloud, and Sage represent more complex integration scenarios. These platforms manage not just accounting but procurement, inventory, and financial planning.
AI invoice processing platforms designed for enterprise deployments offer comprehensive ERP integration that goes beyond simple data export. They can trigger purchase order creation, update inventory levels, and feed into cash flow forecasting models.
Three-way matching becomes automated when the AI platform connects to both procurement and receiving systems. Invoices automatically compare against purchase orders and goods receipts, with discrepancies flagged instantly for resolution.
Payment Platform Integration
The final step in invoice processing is payment. Integration with payment platforms like Bill.com, Tipalti, or banking APIs enables straight-through processing where approved invoices can route directly to payment without manual intervention.
This integration includes payment term management. The system calculates due dates, schedules payments to capture early payment discounts, and sends reminders before deadlines. For recurring invoices, the automation can handle the entire cycle from receipt to payment without human involvement.
The ROI Timeline for AI Invoice Processing
Companies evaluating AI invoice processing need realistic expectations about implementation timelines and return on investment. While benefits accrue quickly, the full value realization follows a predictable pattern.
Months 1-2: Implementation and Training
The first phase involves system setup, integration configuration, and initial training. Modern cloud-based platforms minimize this period, with many organizations processing their first invoices within days of contract signing.
During this phase, the AI learns from your specific invoice formats and business rules. Processing accuracy starts high but improves as the system encounters more examples. Companies typically see 85-90% straight-through processing rates during the first month, rising to 95%+ by month two.
Implementation includes migrating historical invoice data if desired, configuring approval workflows, and training staff on exception handling. Most providers offer implementation support that accelerates this timeline.
Months 3-6: Optimization and Scale
The optimization phase focuses on refining accuracy, expanding automation, and integrating with additional systems. Organizations typically achieve full implementation within this window.
Staff become proficient with the system, processing times continue decreasing, and straight-through processing rates reach optimal levels. This period often reveals opportunities to automate related workflows like vendor onboarding, purchase order management, or payment scheduling.
Companies usually achieve break-even on their investment during this phase. The combination of reduced labor costs, eliminated late fees, captured early payment discounts, and improved cash flow visibility generates measurable savings that offset platform costs.
Months 6-12: Full Value Realization
By the six-month mark, AI invoice processing becomes embedded in daily operations. The system handles routine invoices automatically, staff focus on exceptions and strategic work, and the finance team operates more efficiently.
Full ROI typically occurs within 6-12 months. For mid-sized companies processing 500-1,000 invoices monthly, annual savings of $45,000-75,000 are common when accounting for reduced labor costs, eliminated errors, and improved working capital management.
The value compounds over time. As the AI continues learning from your specific invoices and business rules, accuracy improves, automation rates increase, and the time required for exception handling decreases.
Choosing the Right AI Invoice Processing Solution
Not all AI invoice processing platforms deliver equivalent results. Selecting the right solution requires evaluating multiple factors beyond marketing claims and feature lists.
Accuracy and Reliability
Accuracy represents the most critical factor. Request benchmarks showing performance on invoices similar to yours. Don't accept generic accuracy claims, ask for specific metrics on field-level extraction accuracy, handling of poor-quality documents, and error rates.
Reliability matters just as much as accuracy. The system needs to process invoices consistently every time, not just in ideal conditions. Ask about uptime guarantees, disaster recovery procedures, and what happens when the AI encounters a document type it hasn't seen before.
Integration Capabilities
Evaluate how well the platform connects with your existing technology stack. Pre-built integrations save significant time and cost compared to custom development. Check whether the platform supports your specific accounting software, ERP system, and payment platforms.
API flexibility becomes important as your needs evolve. A platform with robust APIs enables custom integrations, data extraction for reporting, and connections to future systems you might adopt.
Scalability and Volume Handling
Consider both current invoice volume and expected growth. The platform should handle your current needs comfortably while accommodating future expansion without performance degradation or cost explosion.
Concurrent processing capabilities determine how quickly large batches process. Some platforms process invoices sequentially, while others handle hundreds simultaneously. For organizations with month-end invoice spikes, parallel processing prevents bottlenecks.
Security and Compliance
Invoice data contains sensitive financial information requiring robust security. Evaluate encryption practices, access controls, audit trails, and data residency options.
Compliance requirements vary by industry and geography. The platform should support necessary standards like SOX, PCI-DSS, GDPR, or industry-specific regulations. Ask about compliance certifications and how the vendor handles security audits.
Total Cost of Ownership
Look beyond subscription fees to understand complete costs. Implementation fees, integration charges, overage costs, and support pricing all contribute to total ownership cost.
Some platforms charge per invoice processed, while others use seat-based pricing. Calculate costs based on your actual usage patterns to determine which pricing model proves more economical. Factor in the cost of maintaining integrations and upgrading as your needs change.
The Future of AI in Invoice Processing
AI invoice processing continues evolving rapidly. Understanding emerging trends helps organizations plan for the next generation of automation capabilities.
Predictive Analytics and Cash Flow Forecasting
Future systems won't just process invoices, they'll predict payment patterns, forecast cash flow needs, and recommend optimal payment timing. Machine learning models trained on historical payment data can identify which invoices are likely to be paid early, which might run late, and how to optimize working capital.
This predictive capability extends to vendor behavior analysis. The AI can spot trends like vendors who consistently overbill, suppliers whose prices are increasing faster than market rates, or payment terms that could be renegotiated for better terms.
Autonomous Invoice Processing
The trajectory points toward fully autonomous invoice processing where human intervention becomes rare. AI systems will handle not just extraction and validation but also approval routing, exception resolution, and payment execution without human touchpoints.
This autonomy requires AI systems that can explain their decisions, adapt to new situations, and escalate appropriately when genuinely uncertain. The technology exists today in limited deployments and will expand as confidence in AI decision-making grows.
Blockchain Integration for Verification
Blockchain technology offers potential for invoice verification and payment tracking. Smart contracts could automatically validate invoices against purchase orders, trigger payments when conditions are met, and create immutable audit trails.
While blockchain adoption in finance remains early stage, several pilot programs demonstrate how distributed ledger technology can reduce fraud, accelerate payment cycles, and improve transparency across supply chains.
Multimodal AI Understanding
Next-generation AI systems will process not just invoice text but also images, diagrams, handwriting, and even audio or video confirmations of deliveries. This multimodal understanding enables more comprehensive automation of the entire procurement-to-payment cycle.
Computer vision might automatically verify delivered goods against invoice line items, matching physical products to billing. Voice AI could handle vendor inquiries about payment status. These capabilities transform invoice processing from a back-office function to an integrated component of intelligent business operations.
Getting Started with AI Invoice Processing
Organizations ready to implement AI invoice processing should follow a structured approach that minimizes risk while accelerating value realization.
Assess Current State and Define Goals
Document your existing invoice processing workflow in detail. How many invoices do you process monthly? What's the current cost per invoice? Where do errors occur most frequently? How long does the approval cycle take?
Establish specific, measurable goals. Common objectives include reducing processing time by 80%, cutting costs by 70%, achieving 95%+ straight-through processing, and eliminating late payment fees. Clear goals guide solution selection and provide benchmarks for measuring success.
Start with a Pilot Program
Begin with a limited deployment processing a subset of invoices from a specific vendor, department, or invoice type. This pilot validates the technology, identifies integration challenges, and builds organizational confidence before full rollout.
Choose pilot parameters carefully. Select invoices representative of your overall volume but manageable enough to closely monitor. Process 100-200 invoices through the AI system while continuing parallel manual processing to verify accuracy.
Measure, Refine, and Expand
Track key metrics throughout the pilot: extraction accuracy, processing time, error rates, and staff feedback. Use these measurements to refine configuration, adjust business rules, and optimize workflows.
After validating success during the pilot, expand gradually. Add new vendor types, increase volume, and integrate additional systems. This phased approach reduces risk while allowing the AI to learn and improve with each expansion.
Invest in Change Management
Technology implementation succeeds or fails based on organizational adoption. Train staff thoroughly on new workflows, address concerns proactively, and celebrate wins as automation delivers benefits.
Some team members may worry about job security as automation eliminates manual tasks. Frame the change as elevating their roles from data entry to strategic work like vendor negotiation, financial analysis, and process improvement.
Conclusion
AI invoice processing represents one of the most mature and valuable applications of artificial intelligence in business operations. The technology has moved past early adoption into mainstream deployment, with companies of all sizes achieving measurable benefits.
The numbers speak clearly: 95%+ accuracy rates, 80%+ cost reduction, processing times dropping from minutes to seconds, and ROI within 6-12 months. These aren't aspirational goals but proven results that organizations achieve with modern AI platforms.
Success requires choosing the right solution for your specific needs, implementing thoughtfully, and viewing AI as an enhancement to human capabilities rather than a complete replacement. The combination of AI efficiency and human judgment creates invoice processing workflows that are faster, more accurate, and more strategic than either could achieve alone.
For businesses processing hundreds or thousands of invoices monthly, the question isn't whether to adopt AI invoice processing but how quickly to implement it. The competitive advantage, cost savings, and operational improvements make adoption not just beneficial but necessary in 2026's business environment.
Ready to transform your invoice processing with AI? Gennai automatically extracts and processes invoices from your Gmail or Outlook inbox using advanced AI, eliminating manual data entry and reducing processing time by 90%. Start your free trial today and see how AI invoice processing can work for your business.
TL;DR
- AI invoice processing uses computer vision, machine learning, and NLP to extract data with 95-99% accuracy
- Cost savings reach 80%+ dropping from $22.75 per invoice (manual) to ~$2.36 per invoice (AI-powered)
- Processing time drops from 10 minutes to under 30 seconds per invoice with modern AI systems
- Three core technologies: advanced OCR for text recognition, ML for pattern understanding, NLP for context comprehension
- Template-free extraction adapts automatically to new vendor formats without manual configuration
- ROI timeline: break-even in 3-6 months, full value realization within 6-12 months
- Key selection criteria: accuracy benchmarks, integration capabilities, scalability, security compliance, total cost of ownership
- Future trends: predictive analytics, autonomous processing, blockchain verification, multimodal AI
Ready to automate your invoices?
Start extracting invoices from your email automatically with Gennai. Free plan available, no credit card required.
Start FreeRelated Articles
Manual vs Automated AP: The Numbers Don't Lie
Manual vs automated AP compared across 7 key metrics: cost per invoice, processing time, error rate, and more. The data makes the case for automation.
GuideHow to Automate Invoice Processing in 5 Simple Steps
Learn how to automate invoice processing in 5 actionable steps: audit your workflow, connect sources, configure extraction, set approval rules, and optimize.
GuideAccounts Payable Automation: Complete Implementation Guide
Complete guide to accounts payable automation: implementation steps, ROI calculation, phased rollout, and practical advice for finance teams of any size.