Invoice OCR Explained: From Scan to Structured Data
Learn how invoice OCR technology converts scanned documents into structured data. Discover the process, accuracy rates, business benefits, and how to choose the right OCR solution for 2026.

When your finance team drowns in paper invoices every week, something needs to change. Invoice OCR technology transforms how businesses process financial documents by converting scanned images and PDFs into structured, actionable data. This technology now powers modern accounts payable teams worldwide, cutting processing times from hours to seconds.
The transformation from a paper invoice to structured data happens through sophisticated optical character recognition systems that combine computer vision, machine learning, and intelligent data extraction. Understanding how OCR actually works helps finance leaders make better decisions about automation tools and choose solutions that deliver real ROI.
For a beginner-friendly overview of what invoice OCR is and how it benefits businesses, see our complete beginner's guide to invoice OCR. This article takes a deeper, technical look at the process from scan to structured data.
What is Invoice OCR Technology?
Optical Character Recognition for invoices is technology that automatically converts text from scanned documents, PDFs, or images into machine-readable, structured data. Unlike basic document scanning that creates image files, OCR interprets the characters on an invoice and transforms them into editable text that accounting systems can process.
Modern invoice OCR goes far beyond simple character recognition. The technology identifies specific data fields like invoice numbers, dates, vendor information, line items, and amounts. It understands the layout and structure of invoices, even when formats vary significantly between different suppliers.
The global OCR market reached $22.21 billion in 2026 and continues growing at 17.72% annually, projected to hit $60.04 billion by 2032. This explosive growth reflects how critical OCR has become for businesses automating their accounts payable workflows.
Traditional OCR vs AI-Powered OCR
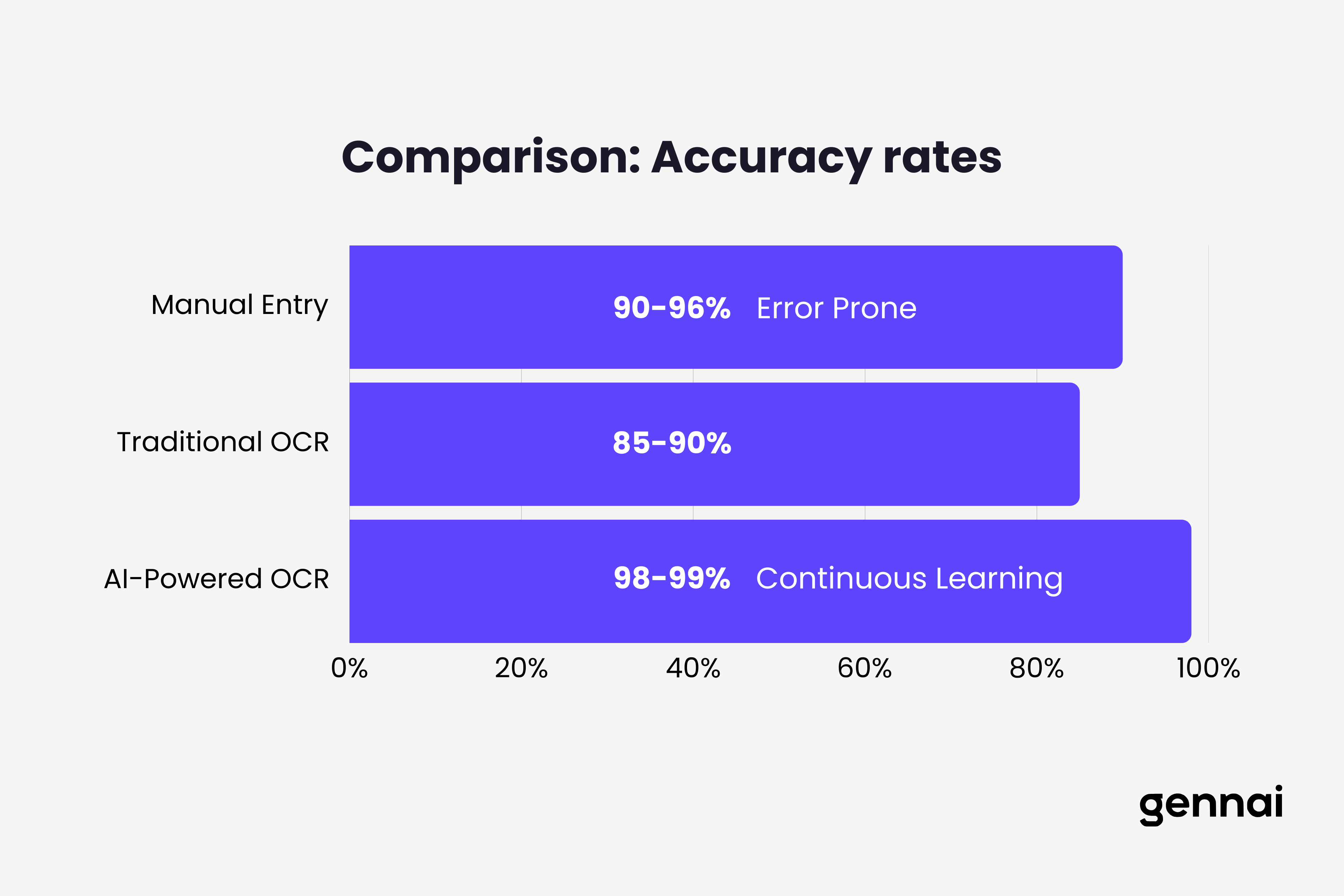
The difference between older OCR systems and modern AI-powered solutions is substantial. Traditional OCR relied on template matching and rigid rules, struggling whenever invoice layouts changed or image quality degraded. These systems typically achieved 85-90% accuracy, leaving significant manual cleanup work for AP teams.
AI-powered OCR leverages machine learning and deep neural networks to understand context and patterns. These systems adapt to new invoice formats without manual template creation and achieve 98-99% accuracy on most documents. They handle variations in fonts, layouts, languages, and even moderate quality issues in scanned images.
The shift to AI-based systems represents a fundamental change in how invoices get processed. Instead of requiring perfect scans and standardized formats, modern OCR works with real-world documents that arrive via email, supplier portals, or mobile photos.
How Invoice OCR Actually Works: The Technical Process
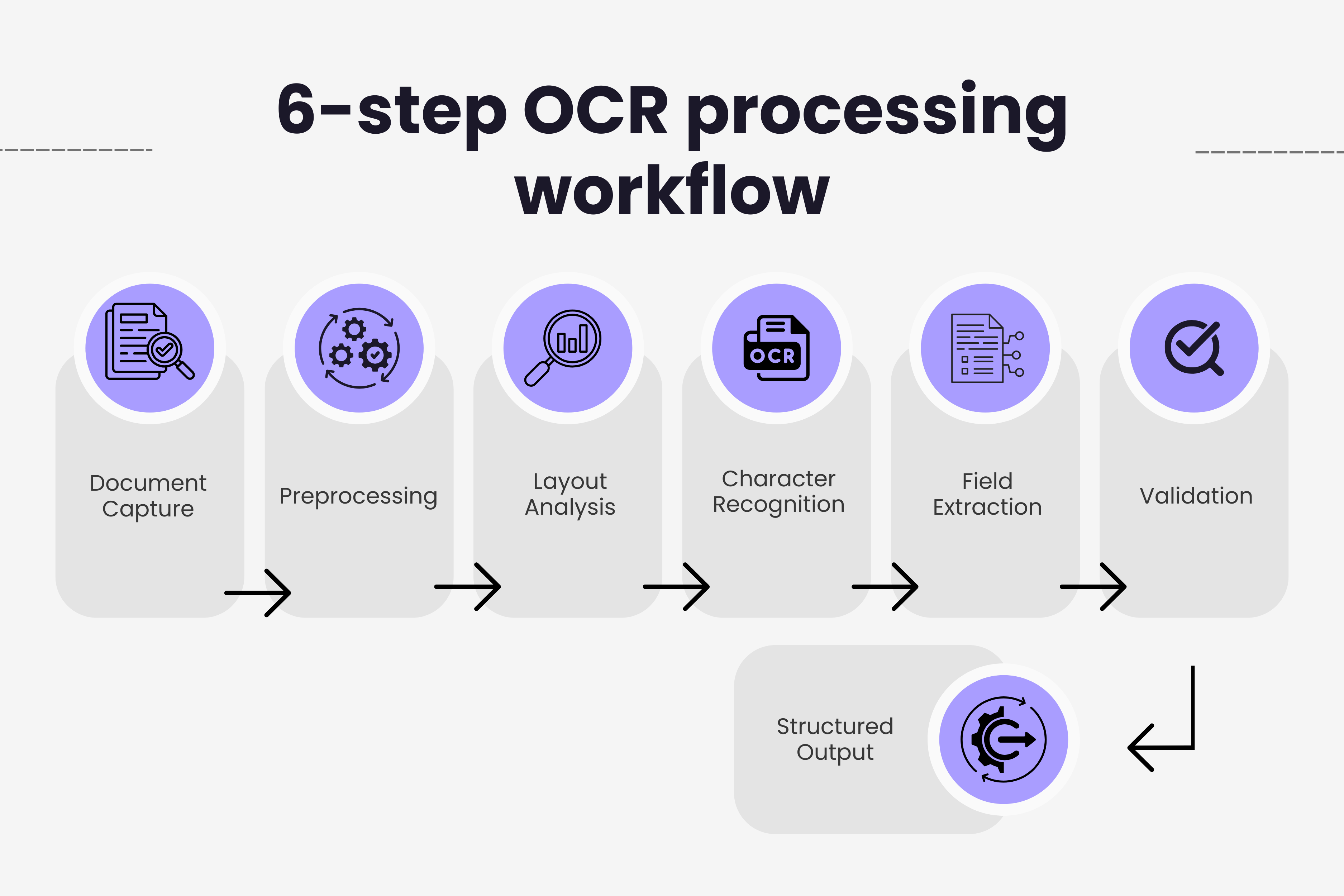
The journey from a scanned invoice to structured data involves multiple sophisticated steps working together seamlessly. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring accurate data extraction.
Step 1: Document Capture and Preprocessing
Invoice processing begins when documents arrive through various channels including email attachments, scanned papers, supplier portals, or mobile camera captures. Modern OCR systems centralize these inputs into a single intake queue.
Before recognition starts, preprocessing algorithms enhance image quality. This critical step includes deskewing tilted scans, removing noise and artifacts, enhancing contrast for better readability, normalizing image resolution, and removing shadows or watermarks that interfere with text recognition.
Quality preprocessing directly impacts extraction accuracy. A well-preprocessed image allows the OCR engine to focus on character recognition instead of fighting image quality issues.
Step 2: Page Layout Analysis
After preprocessing, the system analyzes document structure to understand where different information types appear. Layout analysis identifies text blocks, tables, headers, footers, logos, and signature areas.
This structural understanding helps the OCR engine know where to find critical invoice data. The system learns that invoice numbers typically appear in top sections, line items live in table formats, and totals usually sit at the bottom of documents.
Advanced OCR solutions build contextual maps of invoice layouts. They recognize patterns across thousands of document variations, allowing them to accurately extract data even from invoices they have never seen before.
Step 3: Character Recognition and Text Extraction
The actual text recognition employs multiple techniques working together. Template matching compares characters to predefined patterns, feature extraction identifies key characteristics like lines, curves, and endpoints, and statistical methods analyze character shapes and probabilities.
Modern systems combine these approaches with deep learning models trained on millions of invoice examples. The neural networks recognize characters with high accuracy across different fonts, sizes, handwriting styles, and quality levels.
For invoice processing specifically, OCR engines achieve over 95% accuracy on printed text according to industry benchmarks. When powered by AI and machine learning, top systems reach 98-99% accuracy comparable to human data entry.
Step 4: Intelligent Field Extraction
Raw text extraction is only the beginning. The real value comes from identifying which text belongs to which invoice field. This is where AI-powered OCR demonstrates its advantages over traditional systems.
The extraction engine identifies and captures vendor name and address, invoice number and date, purchase order references, line item descriptions, quantities and unit prices, subtotals and tax amounts, total amount due, and payment terms and due dates.
Unlike template-based systems that look for data in fixed positions, intelligent extraction understands context. It recognizes that a number following "Invoice #" is the invoice number, regardless of where that appears on the page. This contextual understanding allows processing of invoices with vastly different layouts.
Step 5: Data Validation and Verification
After extraction, validation rules ensure accuracy and consistency. The system checks logical correctness like ensuring invoice dates precede due dates, verifies mathematical calculations match, cross-references with purchase orders when available, flags duplicate invoice numbers, and validates against supplier databases.
AI-enhanced OCR assigns confidence scores to extracted fields. Low-confidence fields get flagged for human review, ensuring problematic data doesn't silently enter accounting systems. This exception handling balances automation with accuracy.
Modern platforms process the majority of invoices touchless, with only 10-15% requiring human intervention for complex or unclear cases. This represents a massive improvement over traditional systems that often needed manual review on 30-40% of documents.
Step 6: Structured Data Output and Integration
The final step converts validated data into structured formats that downstream systems consume. OCR platforms export to JSON for API integrations, XML for ERP system feeds, CSV for spreadsheet processing, and direct database inserts for accounting software.
Integration with accounting platforms, ERP systems, and accounts payable software completes the automation loop. Extracted data flows directly into approval workflows, three-way matching processes, and payment systems without manual data entry.
Types of OCR Technology for Invoice Processing
Different OCR approaches suit different business needs. Understanding the options helps organizations choose the right technology for their invoice volumes and complexity.
Template-Based OCR
Template-based systems rely on predefined layouts to extract invoice data. Organizations create templates for each vendor format, defining exactly where each field appears on the invoice. When invoices arrive, the system matches them to templates and extracts data from predetermined locations.
This approach works excellently for businesses receiving invoices from a limited number of vendors with consistent formats. It delivers high accuracy for standard layouts and requires minimal AI infrastructure. The main limitation is rigidity because any layout change breaks the template, requiring manual updates and maintenance.
For companies processing invoices from hundreds or thousands of different suppliers, template maintenance becomes unsustainable. The approach also struggles with variations in invoice designs even from the same vendor.
AI-Powered Free-Form OCR
Free-form OCR uses machine learning to process any invoice format without templates. The system understands invoice structure and context, adapting automatically to new layouts. This flexibility makes it ideal for businesses handling diverse invoice formats.
Modern AI-powered solutions learn continuously from processed documents. They improve accuracy over time, require no template setup or maintenance, and handle format variations effortlessly. The technology processes multilingual invoices and understands context to distinguish similar fields like invoice numbers versus PO numbers.
For businesses interested in the technical details, our guide on machine learning for invoice data explains how these models train and improve over time.
Processing times with AI OCR average 3-5 seconds per invoice according to 2025 benchmarks. Leading platforms like Veryfi achieve 3-4 second response times while maintaining 98%+ accuracy on real-world invoices.
Hybrid OCR Systems
Hybrid approaches combine multiple OCR techniques for maximum flexibility and accuracy. These systems use template-based extraction where applicable, fall back to AI-powered recognition for unknown formats, and employ zonal OCR for semi-structured areas.
The adaptability delivers the highest overall accuracy by selecting the best method for each invoice type. However, hybrid systems require more processing power and configuration complexity compared to pure AI solutions.
Cloud-Based vs On-Premise OCR
Deployment model significantly impacts implementation and ongoing operations. Cloud-based OCR offers instant scalability without hardware investments, automatic updates and improvements, pay-per-use pricing models, and easy integration via APIs.
On-premise solutions provide complete data control for sensitive documents, customization for specific workflows, independence from internet connectivity, and compliance with strict data residency requirements.
The trend strongly favors cloud solutions, with software-based OCR holding 78.8% market adoption due to versatility and AI integration capabilities. Many organizations choose cloud platforms for mainstream processing while maintaining on-premise options for highly sensitive documents.
Real-World Performance: OCR Accuracy and Speed
Understanding realistic performance metrics helps set appropriate expectations for invoice automation initiatives. The numbers from independent benchmarks provide valuable context.
Accuracy Benchmarks
Modern AI-powered OCR consistently achieves 98-99% accuracy on printed invoices in good condition. This matches or exceeds human data entry accuracy, which typically ranges from 90-96% due to fatigue and distraction.
For complex or lower quality invoices, accuracy drops but remains high. Systems handle moderately degraded scans at 95-97% accuracy, multilingual invoices at 93-96% accuracy depending on language, and handwritten notes at 60-75% accuracy for cursive text.
Standalone OCR without AI assistance achieves only 85-90% accuracy, making the difference between modern and legacy systems substantial. The 10-15% accuracy improvement directly translates to fewer manual corrections and faster processing. Understanding why accuracy matters more than speed helps finance teams prioritize the right metrics when evaluating OCR solutions.
Processing Speed Comparisons
Manual invoice processing takes 10-30 minutes per document according to industry studies. AP teams must locate the invoice, identify key fields, manually type data into systems, verify amounts and calculations, and route for approval.
AI-powered OCR reduces this to 1-2 seconds per invoice for automated processing. Even including exceptions requiring human review, average processing time drops dramatically. Best-in-class AP teams now process invoices in 3.1 days versus 17.4 days for organizations using manual methods.
The speed improvement enables same-day invoice processing for the first time at many organizations. Finance teams capture early payment discounts, improve vendor relationships with faster payments, and free staff for strategic work instead of data entry.
Cost Savings Analysis
Processing cost per invoice reveals the dramatic economic impact of OCR automation. Manual processing costs $12-$20 per invoice when accounting for labor, errors, and delays. Organizations using legacy OCR systems spend $5-$8 per invoice due to manual corrections and template maintenance.
AI-powered automation reduces costs to $2-$5 per invoice according to multiple industry benchmarks. For companies processing thousands of invoices monthly, the savings add up quickly. A business processing 5,000 invoices monthly saves $50,000-$90,000 annually by switching from manual to automated OCR.
Beyond direct processing costs, OCR eliminates late payment penalties, captures early payment discounts worth 2-5% of invoice values, and prevents duplicate payments through automated detection.
Common OCR Challenges and How Modern Systems Overcome Them
While OCR technology has advanced significantly, certain challenges still require sophisticated solutions. Understanding these issues helps organizations choose robust platforms.
Handling Invoice Format Variations
Every supplier creates invoices differently. Some use dense tables, others list items vertically. Header placements vary wildly. Color schemes, fonts, and layouts change constantly.
AI-powered OCR overcomes format chaos through contextual understanding. Instead of looking for fields in specific locations, systems recognize patterns and relationships. They understand that amounts with dollar signs represent monetary values regardless of position, dates follow recognizable patterns regardless of format, and line items appear in structured groups with related data.
Machine learning models trained on millions of invoice examples recognize these patterns automatically. The system adapts to new formats without human intervention, continuously improving as it processes more diverse documents.
Managing Poor Image Quality
Real-world invoices arrive in various conditions. Some are high-quality digital PDFs, others are faxed documents from the 1990s, wrinkled papers photographed with smartphones, or invoices with coffee stains and wrinkles.
Modern OCR preprocessing handles these challenges through sophisticated image enhancement. Algorithms automatically correct skew and rotation, remove background noise and artifacts, enhance contrast for faded text, compensate for lighting variations, and sharpen blurred text.
When image quality remains problematic after enhancement, confidence scoring flags uncertain extractions for human review. This prevents poor quality from becoming poor data quality in financial systems.
Extracting Line Item Details
Line items present unique challenges because they appear in tables with varying structures. Some invoices list 5 items, others list 500. Column ordering differs between suppliers. Some include product codes, others don't.
Advanced OCR uses table recognition algorithms specifically designed for invoice line items. The technology identifies table boundaries, recognizes column headers, associates values with correct columns, and handles merged cells and spanning headers.
AI models understand relationships between line item fields. They know quantities multiply by unit prices to calculate line totals, recognize tax rates and applications, and validate that line totals sum to invoice totals.
The Business Impact of Invoice OCR
Understanding ROI helps justify OCR investments and set realistic expectations for automation initiatives. The benefits extend far beyond simple cost reduction.
Productivity Improvements
Finance teams implementing OCR typically experience 30-40% productivity improvements according to research from Harvard Business Review. Staff redirect time from manual data entry to strategic activities like analysis, vendor relationship management, and process optimization.
Automated invoice processing eliminates mundane tasks that drain morale. Team members report higher job satisfaction when freed from repetitive data entry. This improves retention in finance roles where turnover costs organizations significantly.
The scalability proves critical during growth periods or seasonal spikes. OCR systems handle volume increases without requiring additional headcount. Organizations process 2-3 times more invoices with the same team size after implementing automation.
Faster Payment Cycles
Invoice approval cycles shrink from weeks to hours when OCR feeds automated workflows. Data flows instantly from extraction to approval routing to payment processing. No paper moves between desks, no emails get lost, no invoices sit in inboxes waiting for attention.
Faster cycles enable businesses to capture early payment discounts that can reach 2-5% of invoice values. For organizations spending millions annually with suppliers, these discounts represent substantial savings.
Vendor relationships improve when payments arrive predictably and quickly. Suppliers prioritize customers who pay on time, offering better terms, priority service, and flexibility during supply chain disruptions.
Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance
Human data entry achieves 90-96% accuracy at best. The 4-10% error rate creates downstream problems including payment disputes with vendors, accounting reconciliation issues, audit complications, and financial reporting inaccuracies.
OCR automation at 98-99% accuracy cuts error rates by 80-90%. The few errors that occur get caught by validation rules and three-way matching before payments process. This creates cleaner financial data and more reliable reporting.
Compliance benefits include complete audit trails of all invoice processing, automated retention of original documents, standardized approval workflows, and systematic fraud detection through duplicate checking.
Choosing the Right OCR Solution for Your Business
Not all OCR platforms deliver equal results. Organizations should evaluate solutions carefully based on specific needs and priorities. For a detailed comparison of leading platforms including pricing, accuracy benchmarks, and recommendations by business size, see our guide to the best OCR software for invoices in 2026.
Key Features to Evaluate
Accuracy on your actual invoices matters more than vendor claims. Request pilot tests with your real invoice samples from various suppliers. Measure accuracy across different document types and quality levels.
Integration capabilities determine how well OCR fits existing systems. Evaluate API quality and documentation, pre-built connectors for your accounting software, support for your ERP platform, and ease of adding OCR to current workflows.
Processing speed becomes critical at high volumes. Test with realistic batch sizes to understand throughput. Consider both individual invoice speed and concurrent processing capacity.
Questions to Ask Vendors
How does the system handle invoice format variations without templates? What accuracy can you guarantee on our specific invoice types? How quickly does the system process invoices at our typical volumes? What integration options exist for our accounting platform? How do you handle exceptions and low-confidence extractions? What ongoing maintenance does the system require?
Request detailed demos showing actual invoice processing, not just marketing presentations. Watch how the system handles complex invoices, quality issues, and unusual formats.
Implementation Considerations
Successful OCR implementation requires planning beyond technology selection. Consider change management for team members shifting from manual to automated processes, data migration from legacy systems, integration testing with existing workflows, and training for exception handling and system monitoring.
Start with a pilot program processing a subset of invoices. Measure results carefully and refine configurations before full deployment. This staged approach minimizes disruption while proving value.
The Future of Invoice OCR Technology
OCR continues evolving rapidly as AI capabilities advance. Understanding upcoming trends helps organizations prepare for next-generation automation.
Advances in AI and Machine Learning
Current OCR systems already leverage sophisticated neural networks, but the technology keeps improving. Future developments include better handling of completely unstructured documents, enhanced multi-language processing across 100+ languages, improved extraction from handwritten invoices, and deeper contextual understanding of invoice data relationships.
Large language models now contribute to OCR accuracy through semantic comprehension of invoice content. These models understand context in ways traditional OCR never could, recognizing vendor information even when formatted unusually and validating extracted data against business logic.
Integration with Broader Automation
Invoice OCR increasingly connects with end-to-end accounts payable automation platforms. The vision extends beyond data extraction to include automated approval routing based on business rules, intelligent matching with purchase orders and contracts, predictive analytics for cash flow forecasting, and autonomous processing with minimal human intervention.
Companies implementing comprehensive automation achieve touchless processing rates above 90%. Only exceptional cases require human review, dramatically reducing AP department workload.
Mobile and Edge Processing
Mobile OCR applications allow field staff to capture invoices anywhere using smartphones. Edge processing happens on the device itself, eliminating internet dependency and privacy concerns about uploading sensitive documents to cloud servers.
This enables real-time invoice processing at vendor locations, immediate approval workflows while traveling, and offline processing in areas with poor connectivity.
Getting Started with Invoice OCR
Organizations ready to implement OCR should approach the transition strategically for maximum success and ROI.
Assessing Your Current State
Begin by documenting current invoice processing workflows, measuring baseline metrics like processing time per invoice and cost per invoice, identifying pain points and bottlenecks, and quantifying error rates and their impacts.
This baseline data proves crucial for measuring ROI after implementation. Without clear before measurements, organizations struggle to demonstrate value and justify continued investment.
Building the Business Case
Calculate potential savings from reduced labor costs, fewer errors and corrections, eliminated late payment penalties, and captured early payment discounts. Factor in improved vendor relationships and team productivity for intangible benefits.
Most organizations achieve ROI within 3-6 months when implementing automated invoice processing. The payback period shortens for higher invoice volumes and companies currently using manual processes.
Selecting and Implementing Solutions
Choose a vendor aligned with your specific needs, priorities, and existing technology stack. Consider whether you need a standalone OCR tool or a comprehensive AP automation platform that includes OCR as one component.
For businesses already using email-based invoice management, solutions like automated email invoice extraction offer familiar workflows enhanced with OCR capabilities. This approach minimizes change management challenges while delivering automation benefits.
Plan implementation carefully with clear milestones, success metrics, and stakeholder communication. Involve AP team members early to address concerns and gather requirements. Their buy-in proves critical for adoption success.
Conclusion
Invoice OCR has transformed from a nice-to-have efficiency tool into essential infrastructure for modern finance operations. The technology enables processing that would be impossible manually, delivering speed, accuracy, and cost savings that create competitive advantages.
Organizations still processing invoices manually face mounting disadvantages including higher costs per invoice, slower payment cycles that damage vendor relationships, error rates that create compliance risks, and inability to scale operations during growth.
The OCR market's explosive growth to $22.21 billion in 2026 reflects widespread recognition of these realities. Finance leaders understand that automation isn't optional anymore but rather a requirement for operational excellence and competitive survival.
For businesses ready to modernize invoice processing, the path forward combines careful vendor evaluation, strategic implementation planning, and commitment to change management. The result is accounts payable operations that run faster, more accurately, and more cost-effectively than ever possible with manual methods.
Modern OCR solutions like Gennai combine AI-powered extraction with seamless integration to existing workflows. By automatically capturing invoices from email, extracting data with high accuracy, and feeding accounting systems, these platforms deliver the full automation promise that finance teams need.
The question isn't whether to implement invoice OCR but rather when and with which solution. Organizations that act now gain advantages over competitors still stuck in manual processing, while those who wait fall further behind in the efficiency race.
Ready to automate your invoices?
Start extracting invoices from your email automatically with Gennai. Free plan available, no credit card required.
Start FreeRelated Articles
Manual vs Automated AP: The Numbers Don't Lie
Manual vs automated AP compared across 7 key metrics: cost per invoice, processing time, error rate, and more. The data makes the case for automation.
GuideHow to Automate Invoice Processing in 5 Simple Steps
Learn how to automate invoice processing in 5 actionable steps: audit your workflow, connect sources, configure extraction, set approval rules, and optimize.
GuideAccounts Payable Automation: Complete Implementation Guide
Complete guide to accounts payable automation: implementation steps, ROI calculation, phased rollout, and practical advice for finance teams of any size.