Machine Learning for Invoice Data: A Practical Guide
Learn how machine learning extracts invoice data automatically. Practical guide to ML algorithms, training requirements, and continuous improvement for 95%+ accuracy.

Machine learning transforms invoice data extraction from a rule-based process requiring constant manual updates into an intelligent system that improves automatically over time. Unlike traditional OCR that simply recognizes characters, machine learning understands patterns, learns from corrections, and adapts to new invoice formats without explicit programming for each variation. Our complete guide to invoice OCR covers how modern OCR has evolved from simple character recognition to AI-powered systems that work hand-in-hand with machine learning.
The practical difference is enormous. A traditional system requires developers to manually code rules for every vendor's invoice format. A machine learning system trains on examples and automatically recognizes similar patterns in new invoices. When accuracy issues arise, you feed more examples rather than rewriting code. This fundamental shift makes invoice processing scalable across hundreds or thousands of vendors.
We've explored AI invoice processing technology broadly and examined how AI reads invoices technically. Now let's dig into the machine learning mechanics specifically, understanding how models train, improve, and deliver increasingly accurate invoice extraction.
Understanding Machine Learning vs Traditional Rules
Traditional invoice processing operates on explicit rules. The system looks for "Invoice Number:" and captures whatever text follows. It searches for currency symbols followed by numbers to find amounts. Developers write specific logic for table extraction, date parsing, and vendor identification. Every unique invoice layout requires new rules.
Machine learning takes a different approach. You provide thousands of labeled invoice examples showing the AI what invoice numbers, amounts, dates, and line items look like across diverse formats. The algorithm identifies patterns in pixel arrangements, text positioning, surrounding context, and document structure that indicate specific data types.
The ML model learns that invoice numbers tend to be alphanumeric strings appearing near document tops, often near words like "Invoice," "Number," or "Ref." It recognizes that amounts usually appear as numbers with two decimal places, frequently at line ends or in table columns. These patterns generalize across vendors without requiring explicit rules for each format.
When the trained model encounters new invoices, it applies learned patterns rather than searching for hardcoded text strings. An invoice number positioned unusually but sharing pattern characteristics with training data gets correctly identified despite not matching traditional rule-based logic.
This pattern-based approach explains why machine learning handles format variations better than traditional systems. New vendor layouts that would break rule-based extraction often match patterns the ML model already recognizes from training data.
The Core Algorithms Behind Invoice ML
Multiple machine learning algorithms work together in modern invoice processing systems. Understanding which algorithms handle which tasks clarifies how the entire system operates.
Convolutional Neural Networks for Vision
Convolutional neural networks analyze invoice images the way human vision processes scenes. The CNN identifies visual features like edges, shapes, and text blocks before recognizing specific characters. This visual understanding helps the system distinguish tables from headers, locate logos, and understand document structure.
CNNs excel at handling poor image quality, skewed scans, and varying fonts because they recognize character shapes rather than matching exact pixels. The network learns invariant features that remain recognizable across quality levels and formatting variations.
For invoice processing, CNNs typically handle the initial document analysis phase, identifying regions of interest before passing text to specialized extraction algorithms. The CNN might locate the invoice number region, date area, vendor information block, and line item table without reading actual characters.
Transformer Models for Context Understanding
Transformer architectures revolutionized natural language processing and now power invoice field extraction. These models understand relationships between different text elements, recognizing that numbers near "Total:" represent amounts, while identical numbers near "Date:" indicate dates.
The transformer's attention mechanism allows it to focus on relevant context when classifying each field. Processing an invoice number, the model attends to surrounding text like "Inv#" or "Reference" while ignoring irrelevant information elsewhere on the document.
Modern invoice extraction systems often use transformer-based models like BERT or domain-specific variants trained specifically on financial documents. These models achieve 95%+ accuracy on field classification because they understand semantic meaning beyond simple pattern matching.
Named Entity Recognition for Field Identification
Named entity recognition algorithms specifically identify and classify document entities into predefined categories. For invoices, NER models classify text spans as vendor names, addresses, tax identification numbers, payment terms, or line item descriptions.
NER works particularly well for structured documents like invoices where entity types follow predictable patterns. The algorithm learns that text at document tops often represents vendor information, while tabular regions contain line items, and bottom sections show totals.
Training NER models requires labeled datasets marking entity boundaries and types. The model learns statistical patterns indicating where entities begin and end, becoming increasingly accurate as training data expands.
Businesses using email invoice automation benefit from NER's ability to extract complete structured data in a single pass rather than requiring multiple extraction stages.
Training Data: The Foundation of Accuracy
Machine learning models are only as good as their training data. Understanding training data requirements helps explain both capabilities and limitations of ML-based invoice processing.
Quantity Requirements
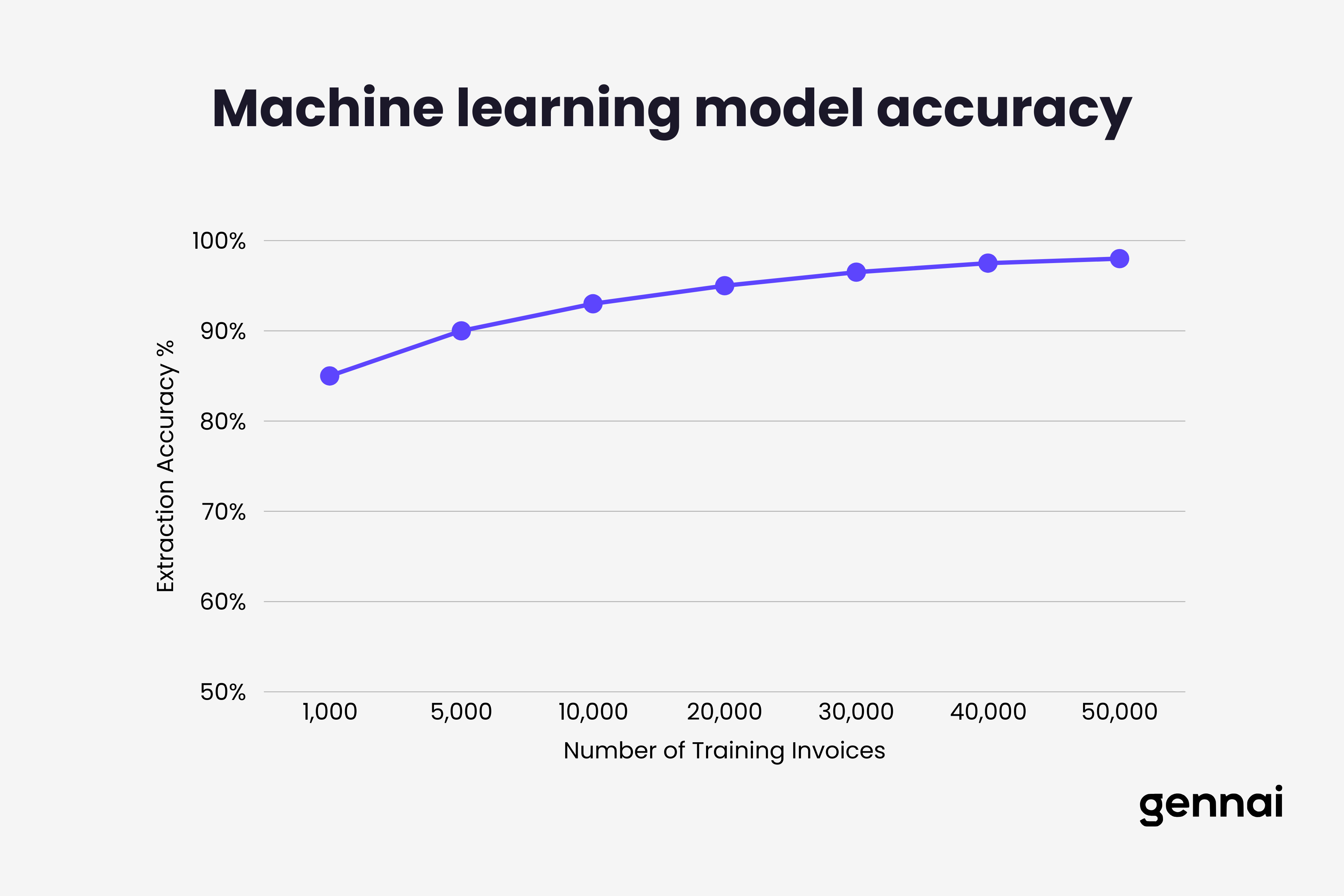
Effective invoice ML models require thousands of training examples. A model trained on 1,000 invoices achieves baseline functionality but struggles with unusual formats. Models trained on 10,000+ diverse invoices handle edge cases more reliably and generalize better to unseen vendors.
The exact quantity depends on invoice diversity. Processing invoices from five similar vendors requires less training data than handling hundreds of vendors across multiple industries and countries. More variation in training data necessitates larger datasets for comparable accuracy.
For businesses evaluating solutions, asking vendors about training dataset size provides insight into model robustness. Systems trained on millions of invoices from thousands of vendors generally outperform those with limited training data.
Quality and Labeling
Training data quality matters more than quantity. Incorrectly labeled examples teach the model wrong patterns, degrading accuracy systematically. A thousand correctly labeled invoices outperform ten thousand with labeling errors.
Professional invoice ML systems employ multi-stage labeling workflows where multiple reviewers validate each annotation. Disagreements get resolved through consensus or expert review. This quality control ensures the model learns correct patterns consistently.
Label quality particularly impacts specific field accuracy. If training data mislabels due dates as invoice dates 10% of the time, the trained model inherits this confusion. Financial ML models require exceptionally high labeling standards because downstream systems depend on perfect field classification.
Diversity and Edge Cases
Training data must represent the full range of invoices the system will encounter in production. A model trained exclusively on simple single-page invoices fails on complex multi-page documents. Systems trained only on English invoices struggle with multilingual documents.
Effective training datasets deliberately include edge cases like handwritten corrections, low-quality scans, unusual layouts, and partially obscured text. These challenging examples teach the model robustness rather than perfect-condition performance that doesn't reflect real-world invoice diversity.
Understanding why AI invoice extraction fails helps identify which edge cases require representation in training data to prevent common failure modes.
The Training Process: From Data to Model
Converting labeled training data into a functioning invoice extraction model involves multiple technical steps. Understanding this process helps set realistic expectations about model development timelines and capabilities.
Data Preprocessing
Raw invoices require preprocessing before model training. PDFs convert to images at consistent resolution. Images undergo enhancement for contrast normalization and skew correction. Text gets extracted via OCR and aligned with visual regions.
This preprocessing creates standardized input the model can process consistently. Without normalization, the model wastes capacity learning to handle format variations rather than focusing on extraction patterns.
Feature Engineering
While deep learning reduces manual feature engineering, invoice ML still benefits from domain-specific features. Positional encodings help the model understand field locations. Table structure detection identifies line item regions. Font size analysis distinguishes headers from details.
These engineered features give the model starting points for pattern recognition. Rather than learning everything from pixel data, the model builds on structured features representing domain knowledge about invoice documents.
Model Architecture Selection
Different neural network architectures suit different extraction tasks. Document classification uses lightweight CNNs. Complex layout analysis requires attention-based transformers. Line item extraction benefits from specialized table-understanding models.
Modern invoice processing systems typically combine multiple architectures. A CNN handles initial document analysis, a transformer extracts field values, and a specialized model processes tables. This ensemble approach leverages each architecture's strengths.
Training and Validation
Model training involves iteratively adjusting neural network parameters to minimize extraction errors on training data. The process typically requires hours or days depending on dataset size and model complexity.
Critical to training success is maintaining separate validation data. The model never sees validation invoices during training, allowing unbiased assessment of generalization performance. Strong training accuracy with poor validation accuracy indicates overfitting, where the model memorized training examples rather than learning generalizable patterns.
Professional ML teams monitor multiple metrics during training including per-field accuracy, confidence score calibration, and processing speed. Training stops when validation performance plateaus, indicating the model has extracted all learnable patterns from available data.
Active Learning: Getting Smarter Over Time
The most powerful aspect of machine learning for invoice processing is continuous improvement through active learning. Unlike static systems requiring manual updates, ML models automatically improve as they process more invoices.
Correction Feedback Loops
When human reviewers correct extraction errors, those corrections become new training data. The next time the model encounters similar invoices, it applies learned corrections rather than repeating mistakes.
This feedback loop accelerates improvement for specific vendor formats that initially caused problems. A vendor whose invoices required manual review initially often processes automatically after the model trains on corrected examples.
Confidence-Based Learning
ML models assign confidence scores indicating certainty about extracted values. Low-confidence extractions flag for human review even if the extracted value appears correct. This conservative approach prioritizes accuracy over automation.
Human validation of low-confidence extractions teaches the model when its uncertainty is justified versus when it's being overly conservative. Over time, confidence calibration improves, reducing unnecessary human review while maintaining accuracy.
Transfer Learning for New Vendors
When processing invoices from entirely new vendors, transfer learning allows models to leverage knowledge from similar existing vendors. The model applies patterns learned from thousands of vendor formats to the new format, achieving reasonable accuracy even on first encounters.
This transfer capability explains why modern ML systems handle new vendors more gracefully than traditional rules-based systems. Rather than requiring explicit configuration for each vendor, the ML model makes educated guesses based on broad invoice pattern knowledge.
Businesses selecting invoice management software should prioritize platforms demonstrating strong transfer learning, as this capability determines how well the system scales to new vendors.
Practical Implementation Considerations
Understanding ML theory helps, but successful invoice processing requires addressing practical implementation challenges.
Computational Requirements
Training invoice ML models demands significant computing resources. GPU acceleration reduces training time from days to hours. Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure provide ML infrastructure eliminating on-premise GPU investment.
For businesses without ML expertise, choosing managed invoice processing services makes more sense than building custom models. The service provider handles model training, updates, and infrastructure while you focus on invoice processing workflows.
Model Maintenance
ML models require ongoing maintenance as invoice patterns evolve. Vendor template changes, new document types, and shifting business requirements necessitate model retraining. Effective systems schedule regular retraining incorporating recent extraction corrections and new vendor formats.
Monitoring model performance over time detects degradation indicating retraining needs. Gradually declining accuracy or increasing manual review rates signal that current training data no longer represents production invoice distribution.
Integration Complexity
ML models output structured data requiring integration with accounting systems, ERP platforms, and payment workflows. API design determines how easily extracted data flows into downstream systems.
Well-designed ML-based invoice systems provide clean JSON or XML output with confidence scores, bounding boxes for verification, and standardized field names. Poor integrations require extensive post-processing defeating ML's efficiency advantages.
Understanding the real cost of manual invoice processing helps justify ML implementation investment when comparing total cost of ownership across solutions.
Choosing ML-Powered Invoice Solutions
When evaluating ML-based invoice processing platforms, specific questions reveal system quality and capabilities.
Ask about training dataset size and diversity. Vendors with millions of training invoices across thousands of companies generally deliver more robust systems than those with limited training data.
Request accuracy metrics on invoices similar to yours. Overall accuracy numbers matter less than performance on your specific invoice types, vendors, and complexity levels.
Understand the feedback loop mechanism. How do corrections improve the model? How frequently does retraining occur? Systems with sophisticated active learning deliver continuously improving performance.
Evaluate confidence scoring quality. Well-calibrated confidence scores accurately predict when extractions need review. Poor calibration results in either missed errors or excessive manual review.
Consider deployment options. Cloud-based ML services provide immediate access to powerful models without infrastructure investment. On-premise deployment offers data privacy but requires maintaining ML infrastructure.
Conclusion
Machine learning fundamentally improves invoice data extraction by replacing rigid rules with learned patterns that generalize across formats and improve automatically over time. The technology isn't magic but rather systematic application of statistical learning to document understanding.
Successful ML-based invoice processing requires substantial training data, appropriate algorithm selection, ongoing model maintenance, and effective feedback loops. These requirements explain why choosing established ML-powered platforms often delivers better results than building custom solutions unless you have significant ML expertise and resources.
The practical impact is clear: ML systems scale to hundreds of vendors without per-vendor configuration, achieve 95%+ accuracy through continuous learning, and reduce manual intervention to genuine exceptions rather than routine processing. For businesses processing significant invoice volumes, ML-powered extraction isn't optional but essential for competitive operation. These ML foundations are now evolving toward autonomous agentic systems that reason across documents and make decisions without human intervention.
Ready to leverage machine learning for invoice processing? Gennai uses advanced AI models with 95%+ accuracy trained on millions of invoices. Our ML systems continuously improve from processing your specific invoice types. Try it free and experience machine learning-powered automation.
TL;DR
- Machine learning replaces rigid rules with learned patterns that generalize across invoice formats and improve automatically over time
- Three core algorithms power invoice ML: CNNs for visual document analysis, transformers for context understanding, and NER for field identification
- Training data quality matters more than quantity — 1,000 correctly labeled invoices outperform 10,000 with labeling errors
- Models trained on 10,000+ diverse invoices handle edge cases reliably; 20,000+ invoices reach the 95% production accuracy threshold
- Active learning creates continuous improvement through correction feedback loops, confidence-based learning, and transfer learning for new vendors
- Transfer learning lets ML systems handle new vendor formats without per-vendor configuration, making them far more scalable than rule-based systems
- Practical considerations include GPU computing requirements, ongoing model maintenance, and clean API integration with accounting systems
- Choose established ML platforms over custom solutions unless you have significant ML expertise — the training data advantage alone justifies managed services
Ready to automate your invoices?
Start extracting invoices from your email automatically with Gennai. Free plan available, no credit card required.
Start FreeRelated Articles
Manual vs Automated AP: The Numbers Don't Lie
Manual vs automated AP compared across 7 key metrics: cost per invoice, processing time, error rate, and more. The data makes the case for automation.
GuideHow to Automate Invoice Processing in 5 Simple Steps
Learn how to automate invoice processing in 5 actionable steps: audit your workflow, connect sources, configure extraction, set approval rules, and optimize.
GuideAccounts Payable Automation: Complete Implementation Guide
Complete guide to accounts payable automation: implementation steps, ROI calculation, phased rollout, and practical advice for finance teams of any size.