How AI Actually Reads Invoices: Behind the Scenes
Discover how AI actually reads invoices through computer vision, OCR, machine learning, and NLP. Technical deep dive into the 4-layer processing system.

When you upload an invoice to an AI processing system, the entire extraction happens in seconds. The vendor name appears, line items populate, totals calculate, and the data flows into your accounting system. But what's actually happening during those seconds? How does AI "read" an invoice when it doesn't have eyes or a brain like humans do?
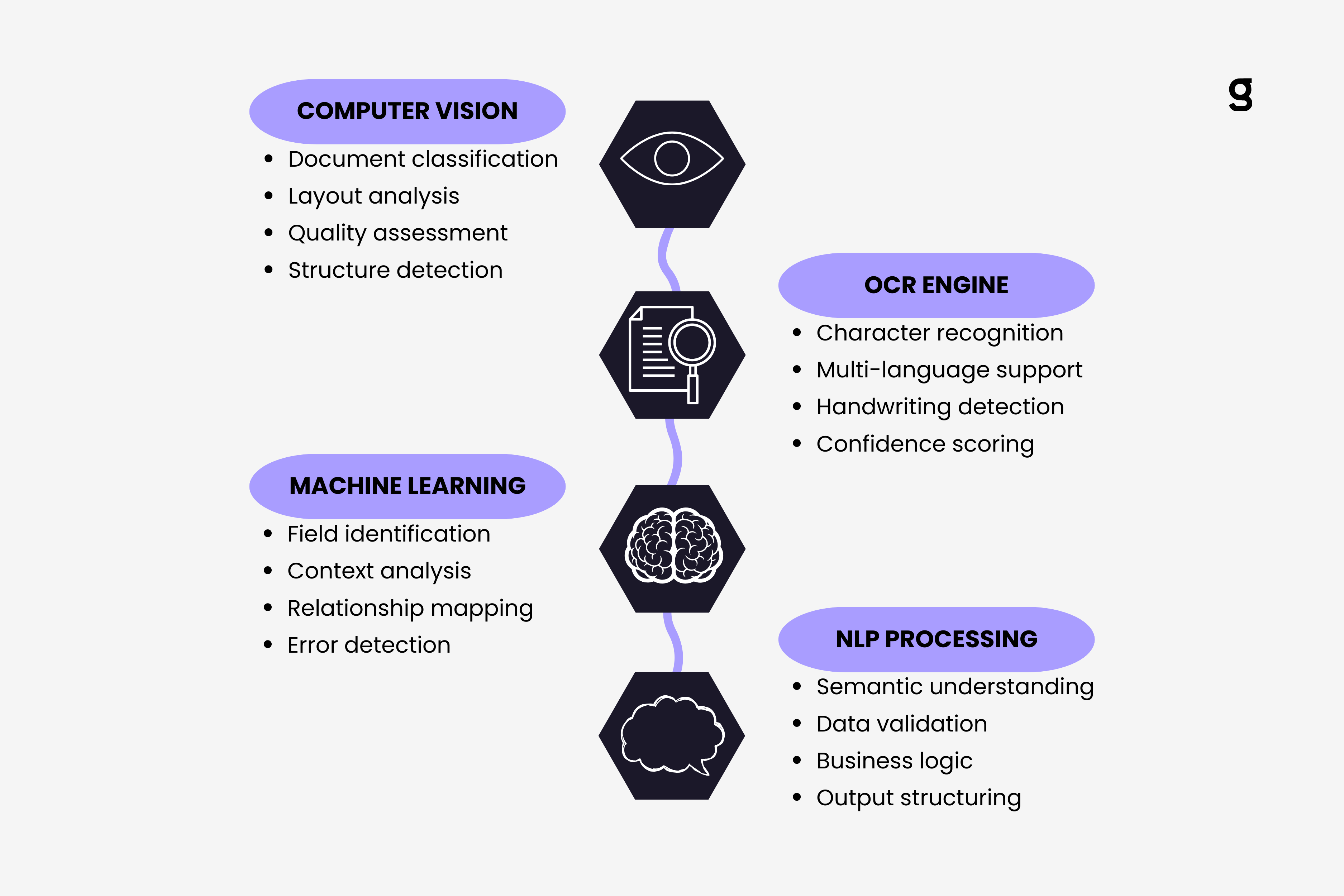
The technology behind AI invoice reading combines multiple sophisticated processes working in sequence. Computer vision analyzes the document structure, optical character recognition converts images to text, machine learning identifies patterns, and natural language processing understands context. Each layer builds on the previous one, creating a system that doesn't just extract characters but actually comprehends what an invoice means.
Understanding this technical process helps explain why modern AI systems perform so much better than traditional OCR tools and why they don't need templates or manual configuration for each vendor format. We covered the complete technical overview of AI invoice processing in our pillar guide. Now let's go deeper into exactly how the reading mechanism works.
The Visual Recognition Phase
Before AI can read any text, it first needs to understand what it's looking at. This initial phase uses computer vision to analyze the document's visual structure, similar to how a human would scan a page before reading the words.
The system starts by detecting the document boundaries and orientation. If an invoice arrives skewed or rotated, the AI automatically corrects the alignment. This preprocessing step ensures the subsequent text extraction works optimally. The vision model identifies whether the document is a single page or multi-page and determines the overall layout structure.
Next comes document classification. The AI needs to confirm this is actually an invoice and not a purchase order, receipt, or contract. Computer vision models trained on millions of financial documents can classify document types with over 95% accuracy by analyzing visual patterns, layouts, and structural elements that are invisible to traditional text-based systems.
The vision layer also performs quality assessment. It evaluates image resolution, contrast, the presence of watermarks or stamps, and potential issues like wrinkled paper or coffee stains. When quality problems are detected, enhancement algorithms automatically adjust contrast, sharpen text, and remove noise before the extraction phase begins.
Document structure analysis happens simultaneously. The AI identifies table regions, header sections, footer areas, and text blocks. This spatial understanding proves crucial for later steps because it helps the system know where different types of information typically appear. A total amount in the top right corner has different meaning than the same number appearing in a line item table.
Think of this phase as the AI building a mental map of the document. It understands the document's geography before attempting to read the individual words. This contextual awareness is what allows modern systems to work without templates. The AI doesn't need to be told where fields appear because it can recognize document structures dynamically.
Text Extraction Layer
Once the computer vision phase completes its analysis, the optical character recognition engine takes over. Modern OCR goes far beyond simple character detection. It employs deep learning models trained specifically on financial documents to achieve accuracy rates above 98% on printed text.
The OCR process happens in parallel across different regions of the document. Header information, line item tables, and footer sections get processed simultaneously, dramatically reducing total processing time. Advanced systems can complete OCR on a standard invoice in under 200 milliseconds.
Character recognition works differently than most people imagine. The AI doesn't match characters to a database of letter shapes. Instead, it uses convolutional neural networks that understand characters in context. The letter "O" and the number "0" look identical in many fonts, but the surrounding context helps the AI determine which one appears in each location.
Multi-language support happens automatically through the OCR layer. Modern systems can process invoices in over 50 languages without requiring language selection. The AI detects the language based on character patterns and switches processing models accordingly. This capability proves essential for international businesses receiving invoices from global vendors.
Handwriting recognition presents unique challenges. While printed text achieves 98%+ accuracy, handwritten notes or corrections typically score between 85-92% accuracy. The system handles this by assigning confidence scores to each extracted character. Handwritten values automatically flag for human review when confidence falls below defined thresholds.
The OCR output includes more than just the extracted text. Each character gets associated with its coordinates on the page, its confidence score, and metadata about font size, style, and formatting. This rich data structure enables the next processing layers to understand relationships between different text elements.
For businesses already using automated invoice extraction from Gmail, understanding this OCR layer helps explain why some invoices process seamlessly while others require review. Poor image quality directly impacts OCR accuracy, which cascades through subsequent processing steps.
Pattern Recognition and Context Understanding
After text extraction completes, machine learning models analyze the extracted content to identify invoice fields and understand their relationships. This layer represents where AI truly differentiates itself from traditional OCR systems.
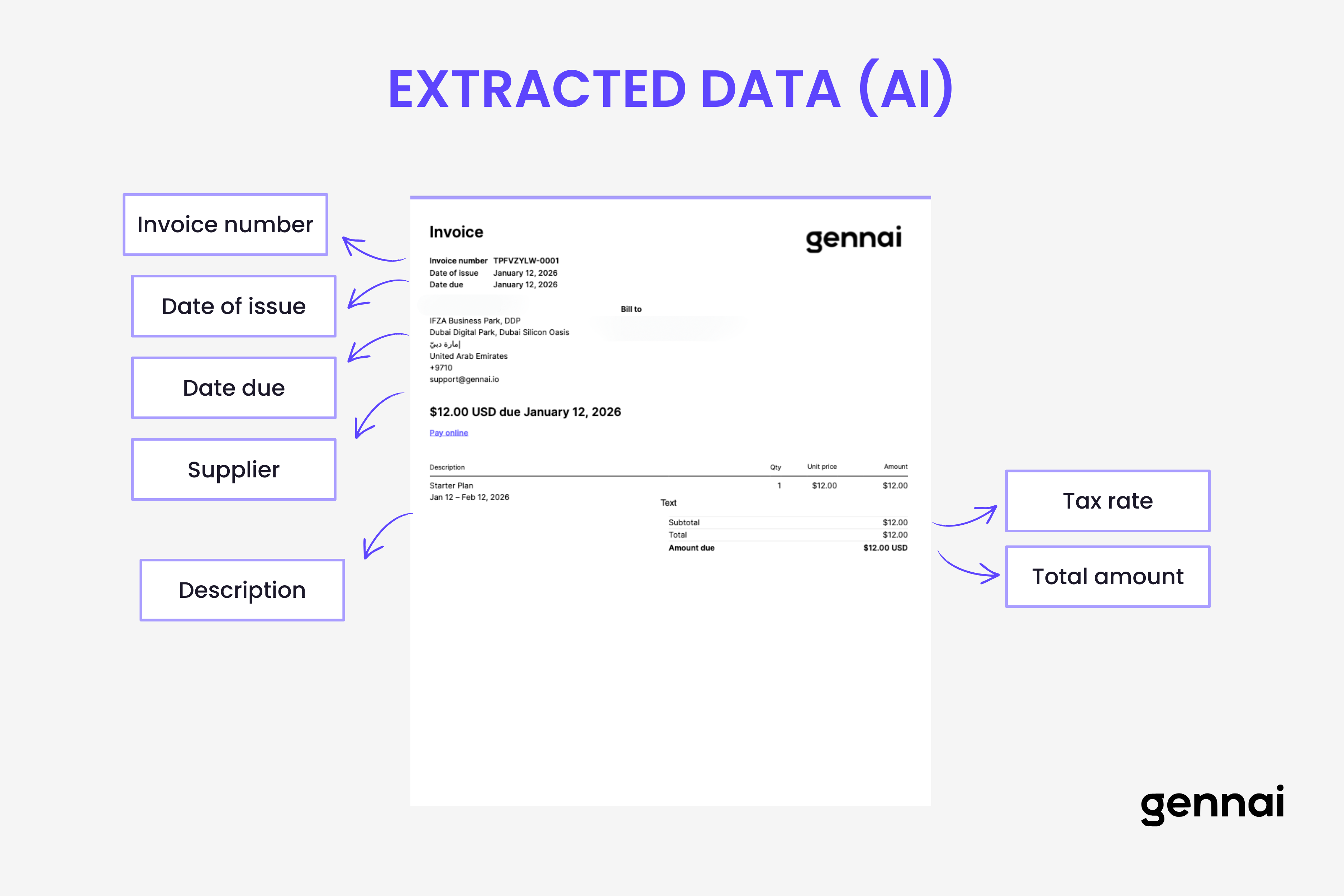
The pattern recognition models have been trained on millions of invoices to understand what different fields look like in various contexts. They don't search for the words "Invoice Number" and assume the next number is the invoice number. Instead, they recognize patterns: invoice numbers tend to be alphanumeric codes appearing near the top of documents, often with specific formatting patterns.
These models understand field relationships. If they identify a date near the text "Due" or "Payment Due," they classify it as a due date rather than an invoice date. When multiple dates appear on an invoice, the AI uses positional context, surrounding text, and learned patterns to distinguish between invoice date, due date, ship date, and payment date.
Table extraction happens through specialized models that understand row and column structures. The AI identifies table boundaries, column headers, and individual cells. It maintains the relationship between quantity, description, unit price, and line total even when table formatting varies dramatically between vendors.
The system builds a semantic graph representing the invoice's information architecture. Vendor details connect to payment terms. Line items link to subtotals. Tax calculations relate to regional rules. This graph structure allows the AI to validate that extracted data makes logical sense.
Confidence scoring occurs at multiple levels. Each individual field receives a confidence score based on how certain the AI is about the extraction. The overall invoice also gets a confidence score indicating how well the entire document was understood. High-confidence invoices route through automated workflows, while low-confidence cases flag for human review.
Mathematical validation happens automatically. The AI verifies that line items sum to stated subtotals, that tax calculations match expected rates, and that all monetary values follow logical patterns. Discrepancies don't necessarily indicate errors but trigger additional scrutiny during the review process.
The Natural Language Processing Layer
The final processing layer applies natural language processing to understand the meaning behind the extracted text. While OCR tells the system what characters appear and ML identifies which field they represent, NLP determines what those fields actually mean.
Semantic understanding allows the AI to interpret variations in how information gets expressed. "Net 30," "Payment due in 30 days," and "30 days from invoice date" all mean the same thing, and NLP models recognize this equivalence. The system normalizes these variations into standard data formats.
Entity recognition identifies specific types of information beyond simple field classification. The AI distinguishes between company names, individual names, addresses, tax identification numbers, and bank account details. This granular understanding enables more sophisticated validation and routing logic.
Business rule validation happens through NLP-powered reasoning. If an invoice shows "Net 30" payment terms but has a due date only 15 days from the invoice date, the AI flags this inconsistency. The system doesn't blindly extract what it sees but applies logical reasoning to validate the data makes business sense.
Multi-currency and international format handling relies heavily on NLP. The AI recognizes date formats from different countries, understands various currency symbols and conventions, and properly interprets number formats whether they use commas or periods as decimal separators.
The NLP layer also handles text normalization. Vendor names might appear as "Acme Corporation," "Acme Corp.," or "ACME CORP" across different invoices. The system recognizes these as the same entity and normalizes them to a consistent format before export to accounting systems.
Output structuring represents the final NLP responsibility. The AI transforms all the extracted, classified, and validated information into the structured format required by the destination system. Whether that's JSON for an API, CSV for spreadsheet import, or direct database entries, the NLP layer handles the formatting automatically.
Understanding the real cost of manual invoice processing makes it clear why this automated NLP layer provides such tremendous value. Tasks that would take humans 5-10 minutes per invoice happen in milliseconds while maintaining higher accuracy.
The Learning Mechanism That Makes It All Work
What makes modern AI invoice reading truly powerful is its ability to learn and improve over time. This isn't static software following rigid rules. The entire system continuously refines its understanding based on new data and corrections.
Active learning happens when humans review and correct low-confidence extractions. Those corrections feed back into the training pipeline, teaching the AI to handle similar situations better in the future. A vendor invoice that required review the first time might process automatically the second time because the system learned the pattern.
Transfer learning allows models trained on millions of generic invoices to quickly adapt to specific vendor formats. Even though your business might work with unique suppliers, the AI leverages knowledge from processing billions of other invoices to understand yours faster. Our practical guide to machine learning for invoice data explores these ML mechanics, training requirements, and continuous improvement processes in detail.
The confidence scoring mechanism creates a virtuous cycle. As the system processes more invoices successfully, its confidence scores become more calibrated. It learns which types of extractions it performs well and which require human verification. This self-awareness prevents overconfident errors while reducing unnecessary human review.
Companies using comprehensive invoice management software with built-in AI benefit from this continuous improvement. The longer the system runs, the smarter it becomes at processing your specific invoice types.
Conclusion
AI invoice reading isn't magic, but it might as well be given how dramatically it improves on traditional methods. The combination of computer vision, OCR, machine learning, and natural language processing creates a system that truly understands invoices rather than just extracting characters.
This multi-layer approach explains why modern AI systems achieve 95-99% accuracy compared to 85-95% for traditional OCR. Each processing layer validates and refines the work of previous layers, catching errors and ambiguities that single-stage systems miss.
For businesses evaluating email invoice automation or AI processing tools, understanding this technical foundation helps explain the capabilities and limitations of different platforms. Systems that implement all these layers will consistently outperform those relying solely on basic OCR. For a comprehensive guide to how OCR technology specifically transforms scanned invoices into structured data, see our complete guide to invoice OCR.
The technology continues evolving rapidly. Next-generation systems will incorporate even more sophisticated reasoning, handle increasingly complex document types, and require progressively less human intervention. Our analysis of the future of AI in financial document processing explores how these capabilities are evolving toward fully autonomous agentic systems. But the fundamental architecture of layered processing will remain the foundation of how AI reads invoices.
Want to see AI invoice reading in action? Gennai processes invoices from your Gmail or Outlook inbox automatically, using the exact technologies described in this article. Try it free and watch your invoices transform from images to structured data in seconds.
TL;DR
- AI invoice reading uses four processing layers: computer vision, OCR, machine learning, and natural language processing
- Computer vision analyzes document structure and classifies document types with 95%+ accuracy
- OCR extracts text with 98%+ accuracy on printed text, processing invoices in under 200 milliseconds
- Machine learning identifies field relationships and validates data using patterns learned from millions of invoices
- NLP understands semantic meaning, normalizes variations, and structures output for destination systems
- Confidence scoring routes high-confidence invoices through automation while flagging uncertain extractions for review
- Active learning continuously improves accuracy as the system processes more invoices and receives corrections
- Modern AI achieves 95-99% accuracy compared to 85-95% for traditional OCR systems
Ready to automate your invoices?
Start extracting invoices from your email automatically with Gennai. Free plan available, no credit card required.
Start FreeRelated Articles
Manual vs Automated AP: The Numbers Don't Lie
Manual vs automated AP compared across 7 key metrics: cost per invoice, processing time, error rate, and more. The data makes the case for automation.
GuideHow to Automate Invoice Processing in 5 Simple Steps
Learn how to automate invoice processing in 5 actionable steps: audit your workflow, connect sources, configure extraction, set approval rules, and optimize.
GuideAccounts Payable Automation: Complete Implementation Guide
Complete guide to accounts payable automation: implementation steps, ROI calculation, phased rollout, and practical advice for finance teams of any size.